A Simple Explanation Of How The Earth Was Formed
Our beautiful planet was born about 4.54 billion years ago. Much has changed since the time when it was nothing more than a collection of rocks and gases. High temperatures, high pressure and explosions… Here we try to give a simple explanation of how scientists today believe that the earth was formed.
Most scientists believe that 13.8 billion years ago, a huge explosion also called the Big Bang occurred. The explosion caused a large amount of matter to explode and move in all directions. Over time, this matter came together to form suns, stars, planets and nebulae… which in turn grouped together to form galaxies.
The formation of planets
From the same cloud of stellar dust, the planet earth and our sun came to form. First, gravity caused the cloud to contract and form small asteroids and then ever larger rocks.
When these larger rocks contracted and fused together, they became primitive planets . And then, as if someone was playing a cosmic game with bullets, they started crashing into each other.

These collisions generated a lot of energy, and this energy together with the elements that made up these primitive planets caused the temperature to increase in their interior and the stone melted. As time went on, the outer layers of the earth began to cool, even though its core would remain blazing hot.
The earth was at just the right distance from the sun for this cooling to occur. But our home planet was still an inhospitable and harsh place. It still lacked a gaseous atmosphere and was full of lava rivers from numerous volcanic eruptions. But this lava did nothing but help make the earth’s crust thicker.
As a result of these volcanic eruptions, the earth’s surface released primordial gases which in turn formed the atmosphere. At this time, however, the atmosphere consisted of hydrogen, helium, methane, ammonium, noble gases and some dispersed oxygen particles.
The formation of water on earth
This incipient oxygen together with atmospheric hydrogen was under optimal pressure and temperature conditions for the next important step in the earth’s evolution. As a result of these conditions, they condensed into the valuable water molecule that makes life on our planet possible. In fact, as far as we know, life without the presence of water is not conceivable.
Land, sea and air fluctuated for a long time until everyone reached their balance and they stabilized in their permanent places. A fiery hot liquid core, oceanic and continental outer crusts and atmospheric gases … these make all planet earth unique, completely unparalleled.
The layers that make up planet earth
The structure of the earth is really what makes it so special. Our planet has four layers with their own substrates, and with an exchange between them all. This makes life on earth possible. But what’s more, the planet earth itself lives and is in a state of constant change.
Geospheres
The geosphere is the layer that includes everything from the center of the earth, the core, to the earth’s crust. The radius of this sphere measures over 6,000 km. It consists of various substrates that include the inner core, the outer core, the upper mantle, the asthenosphere, the lithosphere, and the oceanic and continental crusts.
The biosphere
The biosphere refers to the layer of earth that hosts all living things that inhabit our planet. Rivers, seas, mountains, lakes, deserts… We can find living microbes as deep underwater as 10,984 meters at the bottom of the Marian Tomb, which is the world’s deepest deep sea tomb. At the same time, there are living organisms that live almost a mile above sea level.
The hydrosphere
The hydrosphere is the layer of earth that has water above and below the continental crust. It includes seas, lakes, rivers, oceans, polar ice, water vapor and aquifers.
This layer covers up to 70% of the planet, although only 3% of this water is potable fresh water. The planet’s water passes through a constant cycle involving three states: liquid, solid ice and gas.
The atmosphere
The atmosphere is a layer of gases that characterizes the formation of our planet and acts as a giant dome. It protects us from the sun’s rays and small asteroids from space.
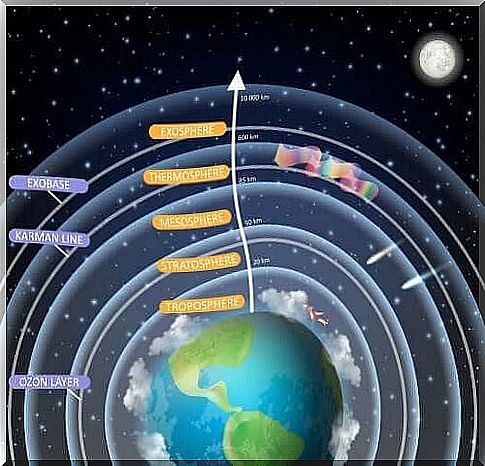
In addition, it gives us the perfect conditions for life thanks to its oxygen-rich composition (21%). This exact percentage varies depending on the layer and divides the atmosphere into three substrates. These are the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, ionosphere and exosphere. All these layers together have a total radius of about 10,000 km.









