Tanning In Children: Why Is It So Dangerous?

Skin cancer is a disease that can be prevented. For this reason, it is important to educate children from an early age about the importance of preventing a tan. Tanning in children not only causes immediate damage but also increases the risk of malignant rashes in the future.
Want to know more about this important topic? Do not miss all the information we have prepared for you.
How to recognize tan in children?
In this article, we use the definition of “tan” as a harmful one. That is, one that leads to redness or is more serious than that.
Light-skinned children are more sensitive to sunburn than dark-skinned children because they have less melanin in the skin. But children with dark skin can also get sunburned.
These injuries caused by UV exposure vary in severity: From mild superficial redness to blisters, severe pain or swelling of the skin (edema).
In general, most sunburn becomes more visible a few hours after the injury has occurred. For this reason , the manifestations cause greater discomfort between 24 and 48 hours after exposure.
The consequences of sunburn in children
In the long run , sunburn in children increases the chance of developing skin cancer, especially melanoma. Even in adults, it promotes premature aging of the skin and the formation of wrinkles from an early age.
Skin cancer
We know that skin cancer is a tumor that grows in the cells of this tissue in an uncontrolled manner. The three most common types of skin cancer include the following:
- Basal cell carcinoma: Highly treatable, slow-growing cancer
- Squamous cell carcinoma: Is more aggressive compared to basal cell carcinoma but is still very treatable
- Melanoma: Can spread much faster.
Although skin cancer is not one of the most common cancers during childhood, the risk of developing it increases by 2% each year. In fact, melanoma accounts for about 3% of all childhood cancers and is closely related to bullous types of burns in childhood and adolescence.
Heatstroke
Heat stroke occurs when the child is directly exposed to high temperatures and for a long time. As a result, the body loses the ability to regulate temperature and dehydrates its tissues.
Some of the typical clinical signs of this condition manifest are the damage that occurred to the central nervous system. Among them stand out the following:
- Loss of balance and impaired gait (ataxia)
- Confusion
- Delirium
- Fittings
A review in Current sports medicine reports concluded that children are more susceptible to heat stroke than adults.

Measures to avoid sunburn in children
The skin contains a natural pigment called melanin, which increases production due to exposure to ultraviolet sunlight. In this way, a darkening of the skin occurs as a typical way to protect it from future sunlight.
But in addition to aesthetic problems, the sun’s rays can cause skin damage that should be avoided. Then we will go into detail about the preventive habits that are important to adopt and instill from childhood.
Avoid exposure at certain times of the day
Children’s skin burns more easily than adults, so special care must be taken. Taking advantage of the shade is always a great way to protect them.
However, it is important to know that certain surfaces (such as sand, water or snow) tend to reflect ultraviolet rays, so hiding under an umbrella or a tree is not always enough.
As a general rule, it is important to avoid sun exposure during the most intense hours of sunshine, ie between 10 and 15.
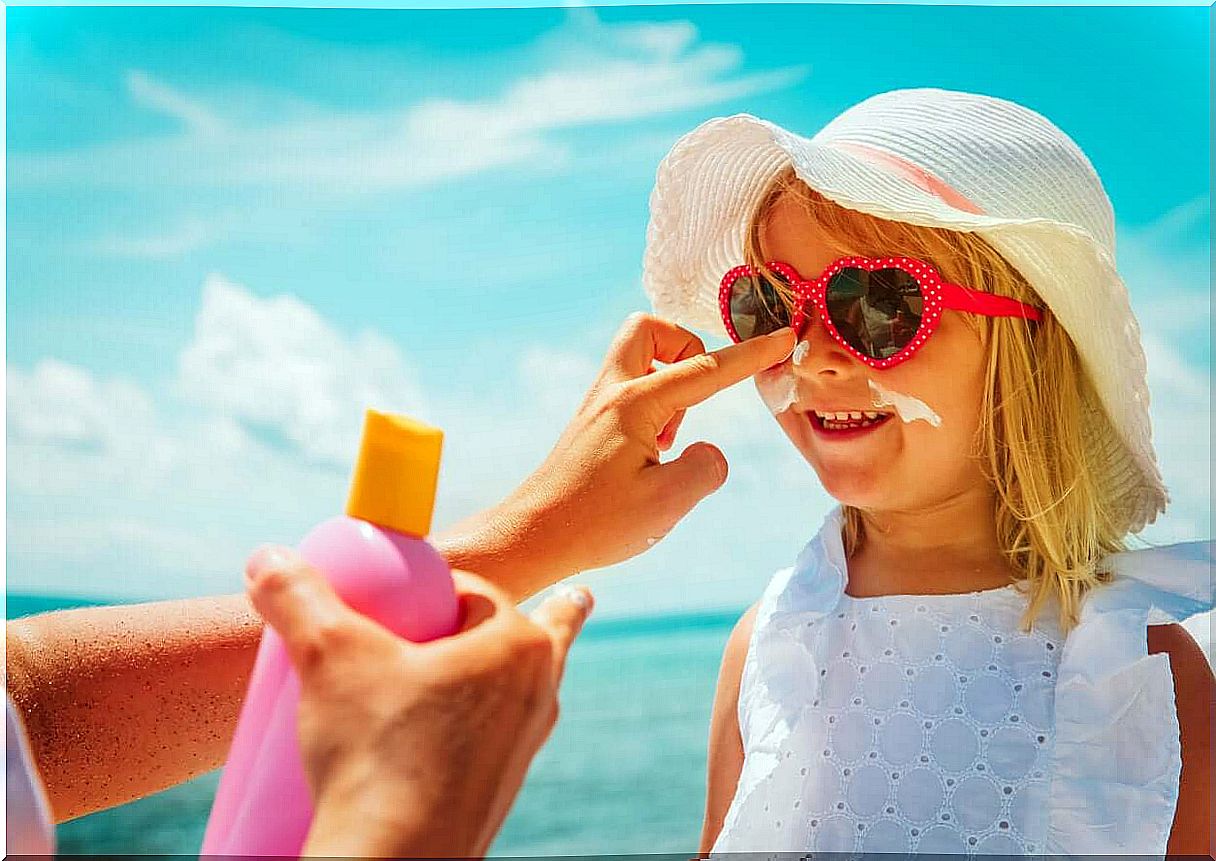
Use of sunscreen
The choice of sunscreen is one of the most important steps in preventing sunburn in children. It must be broad spectrum, with an SPF greater than 30, and waterproof.
Application of sunscreen should be done 30 minutes before sun exposure and be renewed every two hours or earlier if the child becomes sweaty or wet.
However, you should not place these products on the skin of children under 6 months.
Other protective measures
Ideally, your child should cover as much skin as possible with their clothes. Currently, there are a variety of clothing that protects against ultraviolet rays, which has an ultraviolet protection factor (UPF) of 50+.
In turn, the use of hats that protect the neck, face and ears and sunglasses with sun protection are also excellent accessories.

Tanning in children and its future consequences
Sunbathing too much is not a healthy habit and sunburn is actually a sign that the skin has been damaged by ultraviolet rays and is trying to protect itself from even greater damage.
The accumulation of sun damage throughout life significantly increases the chances of developing skin cancer in the future.